Welcome to my new series where I combine the power of Ruby with the discipline of Test-Driven Development (TDD) to tackle popular algorithm problems from LeetCode! 🧑💻💎 Whether you’re a Ruby enthusiast looking to sharpen your problem-solving skills, or a developer curious about how TDD can transform the way you approach coding challenges, you’re in the right place.
🎲 Episode 7: Minimum Size Subarray Sum
###########################################################
# #209
# Given an array of positive integers nums and a positive integer target, return the minimal length of a subarray
# whose @sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
#
# Example 1:
#
# Input: target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
# Output: 2
# Explanation: The subarray [4,3] has the minimal length under the problem constraint.
# Example 2:
#
# Input: target = 4, nums = [1,4,4]
# Output: 1
# Example 3:
#
# Input: target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
# Output: 0
#
#
# Constraints:
#
# 1 <= target <= 109
# 1 <= nums.length <= 105
# 1 <= nums[i] <= 104
#
###########################################################
🔧 Setting up the TDD environment
mkdir minimum-size-subarray-sum
touch minimum-size-subarray-sum/subarray_sum_min_size.rb
touch minimum-size-subarray-sum/test_subarray_sum_min_size.rb
Github Repo: https://github.com/abhilashak/leetcode/tree/main/minimum_size_subarray_sum
❌ Red: Writing the failing test
Test File:
# ❌ Fail
# frozen_string_literal: true
#######################################################
# #209
# Given an array of positive integers nums and a positive integer target, return the minimal length of a subarray
# whose sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
#
#######################################################
require 'minitest/autorun'
require_relative 'subarray_sum_min_size'
class TestSubArraySumMinSize < Minitest::Test
def set_up; end
def test_array_of_length_one
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2], 3).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([2], 2).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([3], 4).min_size
end
end
Source Code:
# frozen_string_literal: true
# disable rubocop GuardClause for better readability in the code
###########################################################
# #209
# Given an array of positive integers nums and a positive integer target, return the minimal length of a subarray
# whose @sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
# ............
#
###########################################################
class SubArray
def min_size
end
end
✗ ruby test_subarray_sum_min_size.rb
Run options: --seed 5914
# Running:
E
Finished in 0.000386s, 2590.6736 runs/s, 0.0000 assertions/s.
1) Error:
TestSubArraySumMinSize#test_array_of_length_one:
ArgumentError: wrong number of arguments (given 2, expected 0)
test_subarray_sum_min_size.rb:16:in 'BasicObject#initialize'
test_subarray_sum_min_size.rb:16:in 'Class#new'
test_subarray_sum_min_size.rb:16:in 'TestSubArraySumMinSize#test_array_of_length_one'
1 runs, 0 assertions, 0 failures, 1 errors, 0 skips
➜ minimum-size-subarray-sum git:(main) ✗
✅ Green: Making it pass
# Pass ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
###########################################################
# #209
# Given an array of positive integers nums and a positive integer target, return the minimal length of a subarray
# whose sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
#
# Example 1:
#........
#
###########################################################
class SubArray
def initialize(nums, target)
@nums = nums
@target = target
end
def min_size
0 if @nums.length == 1 && @nums.first < @target
end
end
✗ ruby minimum-size-subarray-sum/test_subarray_sum_min_size.rb
Run options: --seed 52896
# Running:
.
Finished in 0.000354s, 2824.8588 runs/s, 2824.8588 assertions/s.
1 runs, 1 assertions, 0 failures, 0 errors, 0 skips
………………………………………………….⤵ …………………………………………………………..
# frozen_string_literal: true
# .........
require 'minitest/autorun'
require_relative 'subarray_sum_min_size'
class TestSubArraySumMinSize < Minitest::Test
def set_up; end
def test_array_of_length_one
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2], 3).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([2], 2).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([3], 2).min_size
end
def test_array_of_length_two
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2, 2], 5).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([1, 2], 10).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 2], 4).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([3, 5], 8).min_size
end
end
# Solution for upto 2 Array Input Length ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
###########################################################
# .............
###########################################################
class SubArray
def initialize(nums, target)
@nums = nums
@target = target
end
def min_size
if @nums.length == 1
return (@nums.first == @target ? 1 : 0)
end
@nums.sum == @target ? 2 : 0
end
end
………………………………………………….⤵ …………………………………………………………..
# frozen_string_literal: true
#######################################################
# ..........
#######################################################
require 'minitest/autorun'
require_relative 'subarray_sum_min_size'
class TestSubArraySumMinSize < Minitest::Test
def set_up; end
def test_array_of_length_one
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2], 3).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([2], 2).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([3], 4).min_size
end
def test_array_of_length_two
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2, 2], 5).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([1, 2], 10).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 2], 4).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([3, 5], 8).min_size
end
def test_array_of_length_three
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4], 10).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([12, 3, 9], 10).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4], 7).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4], 4).min_size
end
def test_array_of_length_five
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4, 1, 9], 20).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 3, 9, 1, 0], 10).min_size
assert_equal 4, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4, 6, 4], 17).min_size
assert_equal 5, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4, 12, 10], 31).min_size
end
end
# Solution for upto 5 Array Input Length ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
# disable rubocop GuardClause for better readability in the code
# rubocop:disable Style/GuardClause
###########################################################
# ...............
###########################################################
class SubArray
def initialize(nums, target)
@nums = nums
@target = target
@min_length = 0 # default 0 -> solution not found
@left_pos = 0
@right_pos = 0
@sum = nil
end
def min_size
while @right_pos < @nums.length
# first position where left and right positions are at starting point
@sum = if @left_pos.zero? && @right_pos.zero?
@nums[@right_pos]
else
# add elements inside the window
@nums[@left_pos..@right_pos].sum
end
if solution_found?
update_min_length
return 1 if @min_length == 1 # best scenario found, stop here
else
@right_pos += 1 # increase window size by 1
end
end
@min_length
end
private
def update_min_length
new_length = @right_pos - @left_pos + 1
if min_length_empty? || min_or_equal_length?(new_length)
@min_length = new_length
@left_pos += 1
end
end
def solution_found?
@sum >= @target
end
def min_length_empty?
@min_length.zero?
end
# if new length of subarray found is less than already found min length
# or new length found is equal to previous min length (should decrease window size
# by increasing left pos to find the less length subarray)
def min_or_equal_length?(new_length)
new_length <= @min_length
end
end
………………………………………………….⤵ …………………………………………………………..
# Test Cases with Original LeetCode examples, Edge Cases, Additional test cases
# frozen_string_literal: true
#######################################################
# ..........
#######################################################
require 'minitest/autorun'
require_relative 'subarray_sum_min_size'
class TestSubArraySumMinSize < Minitest::Test
def set_up; end
def test_array_of_length_one
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2], 3).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([2], 2).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([3], 4).min_size
end
def test_array_of_length_two
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2, 2], 5).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([1, 2], 10).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 2], 4).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([3, 5], 8).min_size
end
def test_array_of_length_three
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4], 10).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([12, 3, 9], 10).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4], 7).min_size
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4], 4).min_size
end
def test_array_of_length_five
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4, 1, 9], 20).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 3, 9, 1, 0], 10).min_size
assert_equal 4, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4, 6, 4], 17).min_size
assert_equal 5, SubArray.new([2, 3, 4, 12, 10], 31).min_size
end
# Original LeetCode examples
def test_leetcode_example1
# Input: target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
# Output: 2 (subarray [4,3])
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3], 7).min_size
end
def test_leetcode_example2
# Input: target = 4, nums = [1,4,4]
# Output: 1 (subarray [4])
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([1, 4, 4], 4).min_size
end
def test_leetcode_example3
# Input: target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
# Output: 0 (no subarray sums to >= 11)
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], 11).min_size
end
# Edge cases
def test_empty_array
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([], 5).min_size
end
def test_target_zero
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([1, 2, 3], 0).min_size
end
def test_target_equals_single_element
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([5, 2, 3], 5).min_size
end
def test_target_equals_array_sum
assert_equal 3, SubArray.new([1, 2, 3], 6).min_size
end
def test_target_greater_than_array_sum
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([1, 2, 3], 10).min_size
end
# Additional test cases
def test_consecutive_ones
assert_equal 3, SubArray.new([1, 1, 1, 1, 1], 3).min_size
assert_equal 5, SubArray.new([1, 1, 1, 1, 1], 5).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([1, 1, 1, 1, 1], 6).min_size
end
def test_large_numbers
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([100, 1, 1, 1], 50).min_size
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([50, 50, 1, 1], 100).min_size
end
def test_window_shrinking
# Test that the algorithm properly shrinks the window
# [1, 4, 4] with target 4 should return 1, not 2
assert_equal 1, SubArray.new([1, 4, 4], 4).min_size
end
def test_multiple_valid_subarrays
# [2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3] with target 7
# Valid subarrays: [2,3,1,2] (sum=8), [4,3] (sum=7), [3,1,2,4] (sum=10)
# Should return 2 (shortest: [4,3])
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3], 7).min_size
end
def test_all_elements_equal
assert_equal 2, SubArray.new([3, 3, 3, 3], 6).min_size
assert_equal 3, SubArray.new([3, 3, 3, 3], 9).min_size
assert_equal 0, SubArray.new([3, 3, 3, 3], 13).min_size
end
end
# Solution 1 ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
# disable rubocop GuardClause for better readability in the code
# rubocop:disable Style/GuardClause
###########################################################
# #209
# .............
###########################################################
class SubArray
def initialize(nums, target)
@nums = nums
@target = target
@min_length = 0 # default 0 -> solution not found
@left_pos = 0
@right_pos = 0
@sum = nil
end
def min_size
while @right_pos < @nums.length
@sum = calculate_sum
if solution_found?
update_min_length
return 1 if @min_length == 1 # best scenario found, stop here
else
@right_pos += 1 # increase window size by 1
end
end
@min_length
end
private
def calculate_sum
# first position where left and right positions are at starting point
return @nums[@right_pos] if @left_pos.zero? && @right_pos.zero?
# add elements inside the window
@nums[@left_pos..@right_pos].sum
end
def update_min_length
new_length = @right_pos - @left_pos + 1
if min_length_empty? || min_or_equal_length?(new_length)
@min_length = new_length
@left_pos += 1
end
end
def solution_found?
@sum >= @target
end
def min_length_empty?
@min_length.zero?
end
# if new length of subarray found is less than already found min length
# or new length found is equal to previous min length (should decrease window size
# by increasing left pos to find the less length subarray)
def min_or_equal_length?(new_length)
new_length <= @min_length
end
end
# Solution 2 ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
# disable rubocop GuardClause for better readability in the code
###########################################################
# #209
# .............
###########################################################
class SubArray
def initialize(nums, target)
@nums = nums
@target = target
@min_length = 0 # default 0 -> solution not found
@left_pos = 0
@right_pos = 0
@sum = nil
end
def min_size
while @right_pos < @nums.length
@sum = calculate_sum
if solution_found?
update_min_length
return 1 if @min_length == 1 # best scenario found, stop here
else
@right_pos += 1 # increase window size by 1
end
end
@min_length
end
private
def calculate_sum
# first position where left and right positions are at starting point
return @nums[@right_pos] if @left_pos.zero? && @right_pos.zero?
# add elements inside the window
@nums[@left_pos..@right_pos].sum
end
def update_min_length
new_length = @right_pos - @left_pos + 1
@min_length = new_length if min_length_empty? || min_length_greater?(new_length)
@left_pos += 1
end
def solution_found?
@sum >= @target
end
def min_length_empty?
@min_length.zero?
end
# if new length of subarray found is less than already found min length
# or new length found is equal to previous min length (should decrease window size
# by increasing left pos to find the less length subarray)
def min_length_greater?(new_length)
@min_length > new_length
end
end
🧮 Algorithm Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n²)
Our current algorithm has quadratic time complexity due to the calculate_sum method:
def calculate_sum(nums, left_pos, right_pos)
# This line causes O(n) complexity in each iteration
nums[left_pos..right_pos].sum
end
Why O(n²)?
- Outer loop:
while right_pos < nums.length→ O(n) - Inner operation:
nums[left_pos..right_pos].sum→ O(n) - Total: O(n) × O(n) = O(n²)
Solution: We should change this logic of repeated addition of numbers that are already added before. We can add the next Number (Right position) and substract the Left Number that is out of the window.
Space Complexity: O(1)
- Only uses a constant number of variables regardless of input size
- No additional data structures that grow with input
🚀 Optimized Version (O(n) Time):
Here’s how to make it linear time complexity:
Let’s Try to Optimize our solution with the Solution given above:
# frozen_string_literal: true
# disable rubocop GuardClause for better readability in the code
###########################################################
# ..................
###########################################################
class SubArray
def initialize(nums, target)
@nums = nums
@target = target
@min_length = 0 # default 0 -> solution not found
@left_pos = 0
@right_pos = 0
@sum = 0
end
def min_size
while @right_pos < @nums.length
# Add the new element at right_pos to the current sum
@sum += @nums[@right_pos]
update_min_length if solution_found?
@right_pos += 1 # always move right pointer
end
@min_length
end
private
def update_min_length
new_length = @right_pos - @left_pos + 1
@min_length = new_length if min_length_empty? || min_length_greater?(new_length)
# Shrink the window from the left as much as possible while maintaining sum >= target
while @left_pos < @right_pos && (@sum - @nums[@left_pos]) >= @target
@sum -= @nums[@left_pos]
@left_pos += 1
new_length = @right_pos - @left_pos + 1
@min_length = new_length if min_length_greater?(new_length)
end
end
def solution_found?
@sum >= @target
end
def min_length_empty?
@min_length.zero?
end
# if new length of subarray found is less than already found min length
# or new length found is equal to previous min length (should decrease window size
# by increasing left pos to find the less length subarray)
def min_length_greater?(new_length)
@min_length > new_length
end
end
📊 Complexity Comparison:
| Version | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Why |
|---|---|---|---|
| Your Current | O(n²) | O(1) | Recalculates sum each time |
| Optimized | O(n) | O(1) | Maintains running sum |
Key Optimization:
Instead of recalculating the sum each time:
# Your approach (O(n) each time)
nums[left_pos..right_pos].sum
# Optimized approach (O(1) each time)
current_sum += num # Add new element
current_sum -= nums[left] # Remove old element
Our algorithm works correctly but can be optimized from O(n²) to O(n) time complexity!
LeetCode Submission (simplified version of 0(n)):
# @param {Integer} target
# @param {Integer[]} nums
# @return {Integer}
def min_sub_array_len(target, nums)
return 0 if nums.empty?
min_length = Float::INFINITY
left = 0
sum = 0
nums.each_with_index do |num, right|
sum += num
# Shrink window from left as much as possible while maintaining sum >= target
while sum >= target && left <= right
min_length = [min_length, right - left + 1].min
sum -= nums[left]
left += 1
end
end
min_length == Float::INFINITY ? 0 : min_length
end
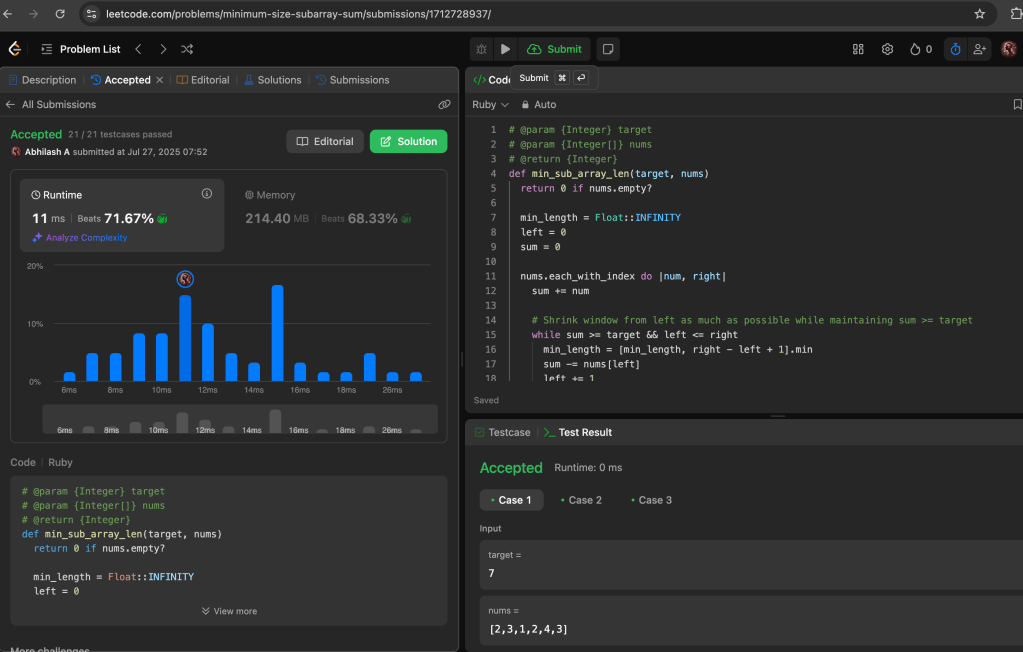
The Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/description/
The Solution: https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/description/?submissionId=1712728937
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/submissions/1712728937/
Happy Algo Coding! 🚀