Welcome to my new series where I combine the power of Ruby with the discipline of Test-Driven Development (TDD) to tackle popular algorithm problems from LeetCode! 🧑💻💎 Whether you’re a Ruby enthusiast looking to sharpen your problem-solving skills, or a developer curious about how TDD can transform the way you approach coding challenges, you’re in the right place.
🎲 Episode 3: Contains Duplicate
# Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears # at least twice in the array, and return false if every element # is distinct.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: true
Explanation:
The element 1 occurs at the indices 0 and 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: false
Explanation:
All elements are distinct.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2]
Output: true
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
🔧 Setting up the TDD environment
Create files and folder
mkdir array_duplicate
touch array_duplicate.rb
touch test_array_duplicate.rb
# frozen_string_literal: true
require 'minitest/autorun'
require_relative 'buy_sell'
#####################
##
#####################
# frozen_string_literal: true
#####################
❌ Red: Writing the failing test
# frozen_string_literal: true
require 'minitest/autorun'
require_relative 'array_duplicate'
######################################
#
#
#
######################################
class TestArrayDuplicate < Minitest::Test
def setup
####
end
def test_array_with_length_one
assert_equal false, Duplicate.new([]).present?
end
end
✗ ruby array_duplicate/test_array_duplicate.rb
Run options: --seed 27633
# Running:
E
Finished in 0.000491s, 2036.6599 runs/s, 0.0000 assertions/s.
1) Error:
TestArrayDuplicate#test_array_with_length_one:
NameError: uninitialized constant TestArrayDuplicate::Duplicate
array_duplicate/test_array_duplicate.rb:16:in 'TestArrayDuplicate#test_array_with_length_one'
1 runs, 0 assertions, 0 failures, 1 errors, 0 skips
✅ Green: Making it pass
# Pass ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
#############################
#
# Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array,
# and return false if every element is distinct.
# Example 1:
# .......
#############################
class Duplicate
def initialize(nums)
@numbers = nums
end
def present?
'Provide a non-empty array' if @numbers.empty?
end
end
…………………………………………………. ⤵ …………………………………………………………..
Writing the Second Test Case:
# frozen_string_literal: true
require 'minitest/autorun'
require_relative 'array_duplicate'
######################################
# Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array,
# and return false if every element is distinct.
#
# Example 1:
# Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
# Output: true
#
# Example 2:
# Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
# Output: false
#
######################################
class TestArrayDuplicate < Minitest::Test
def setup
####
end
def test_empty_array
assert_equal 'Provide a non-empty array', Duplicate.new([]).present?
end
def test_array_with_length_one
assert_equal false, Duplicate.new([2]).present?
end
def test_array_with_length_two
assert_equal false, Duplicate.new([1, 2]).present?
assert_equal true, Duplicate.new([2, 2]).present?
end
end
# Solution 1 ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
#############################
#
# Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array,
# and return false if every element is distinct.
# Example 1:
# ........
#############################
class Duplicate
def initialize(nums)
@numbers = nums
end
def present?
return 'Provide a non-empty array' if @numbers.empty?
count_hash = {}
@numbers.each do |number|
count_hash[number] ? count_hash[number] += 1 : count_hash[number] = 1
end
count_hash.values.max > 1
end
end
⏳ Finding the Time Complexity
Time Complexity: O(n)
- You iterate through the array once: @numbers.each do |number| → O(n)
- Hash operations (lookup and assignment) are O(1) on average
- count_hash.values.max → O(n) to get all values and find max
- Total: O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
- In worst case (all elements are unique), you store n key-value pairs in count_hash
- Total: O(n)
♻️ Refactor: Optimizing the solution
# Solution 2 ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
#############################
#
# Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array,
# and return false if every element is distinct.
# Example 1:
# .....
#############################
class Duplicate
def initialize(nums)
@numbers = nums
end
def present?
return 'Provide a non-empty array' if @numbers.empty?
count_hash = {}
@numbers.each do |number|
count_hash[number] ? count_hash[number] += 1 : count_hash[number] = 1
return true if count_hash[number] > 1
end
false
end
end
♻️ Refactor: Try to refactor the solution again
# Solution 3 ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
#############################
#
# Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array,
# and return false if every element is distinct.
# Example 1:
# Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
# .......
#############################
class Duplicate
def initialize(nums)
@numbers = nums
end
def present?
return 'Provide a non-empty array' if @numbers.empty?
found = {}
@numbers.each do |number|
return true if found[number]
found[number] = true
end
false
end
end
♻️ Refactor: Use Ruby Set – best approach
# Solution 4 ✅
# frozen_string_literal: true
#############################
#
# Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array,
# and return false if every element is distinct.
# Example 1:
# Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
# ........
#############################
class Duplicate
def initialize(nums)
@numbers = nums
end
def present?
return 'Provide a non-empty array' if @numbers.empty?
found = Set.new
@numbers.each do |number|
return true if found.include?(number)
found.add(number)
end
false
end
end
Set vs Hash for Duplicate Detection
Set Approach:
seen = Set.new
@numbers.each do |number|
return true if seen.include?(number)
seen.add(number)
end
Hash Approach:
seen = {}
@numbers.each do |number|
return true if seen[number]
seen[number] = true
end
Why Set is Better for This Use Case:
1. Semantic Clarity
- Set: Designed specifically for storing unique elements
- Hash: Designed for key-value mappings
- Since we only care about “have I seen this number?”, Set is semantically correct
2. Memory Efficiency
- Set: Only stores the key (the number)
- Hash: Stores both key AND value (number + true/false)
- Set uses less memory per element
3. Intent is Clearer
# Set - clearly shows we're tracking unique elements
seen.add(number)
seen.include?(number)
# Hash - less clear why we're setting values to true
seen[number] = true
seen[number] # relies on truthy/falsy behavior
4. Performance
Both have O(1) average lookup time, but:
- Set operations are optimized for membership testing
- Hash has slight overhead for value storage
When to Use Each:
Use Set when:
- You only need to track “presence” or “membership”
- You want to store unique elements
- You don’t need associated values
- This duplicate detection problem ✅
Use Hash when:
- You need to store key-value pairs
- You need to count occurrences
- You need to associate data with keys
- Example:
{number => count}for frequency counting
Alternative Hash Approach (Still Valid):
If you prefer Hash, this is also perfectly fine:
seen = {}
@numbers.each do |number|
return true if seen.key?(number) # More explicit than seen[number]
seen[number] = true
end
Bottom Line:
Both work correctly with the same time/space complexity, but Set is the better choice because:
- It’s semantically correct for the problem
- Uses less memory
- Makes the code’s intent clearer
- Is specifically designed for this use case
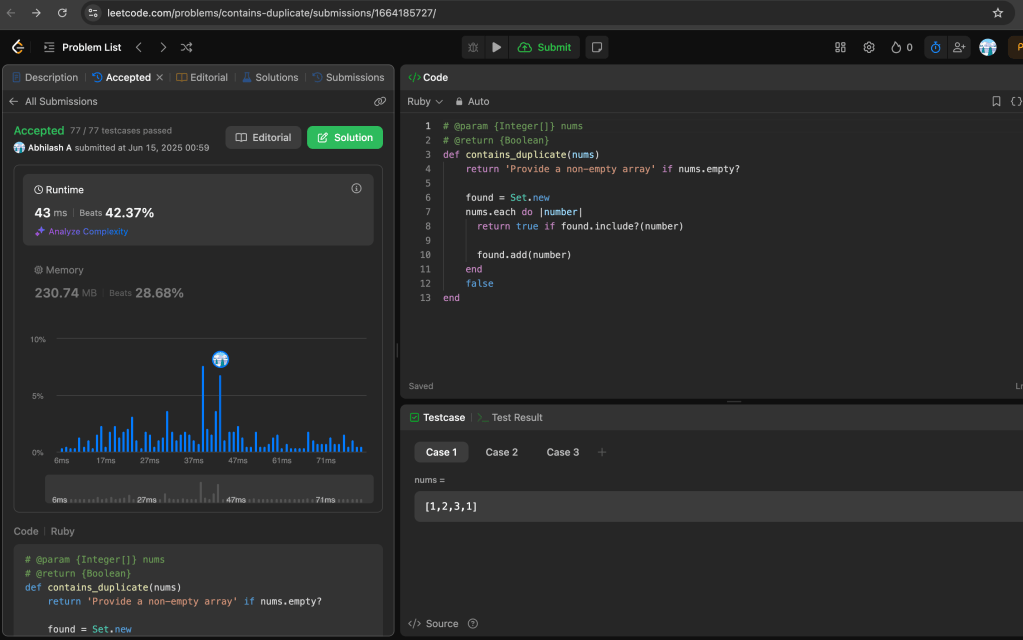

The Problem: https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate/description/
The Solution: https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate/post-solution/?submissionId=1664185727
https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate/submissions/1664185727/
Happy Algo Coding! 🚀
